|
|
Marketing’s
Seven P’s |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Learning Objectives: Upon completing of this unit,
the student will be able to: ● Define a product, product line and
product mix and give examples of product classifications. ● Explain the benefits of branding
and discuss strategies for successful branding. ● Discuss the decisions
surrounding the product’s packaging and how those decisions are impacted by the global
marketplace ● List and explain the steps in the
new product development process. ● Describe the stages of
the product life cycle and how marketing strategies change during each stage. ● Distinguish between goods and
services and explain marketing issues unique to services. |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
TOPIC:
MARKETING MIX As a
family consisting of father, mother, sons, daughters and grandparents,
playing an important role in bringing up of a newly born child in the family,
so that the child does not become a misfit in society, so is every element of
marketing mix to a product/service. Definition: o
“Marketing Mix is the ability of how an organisation combines factors that allow it to gain an
advantage over their competitors, it is this combination of factors that an organisation controls to provide value to its target
customers”. o
“Marketing Mixis the set of tactical marketing tools: product,
price, place, promotion, people, physical evidence and process that the firm
blends to produce the response it wants in the target market”. o
“Marketing Mix is the combination of marketing elements
used by a business to enable it to meet the needs and expectations of
customers o
Philip Kotlerdefined the “Marketing Mix” as
the set of controllable variables a firm can use to influence buyer response. It is
called a Marketing Mix: o
Because each element of the marketing mix is related to the
others o
Elements of the mix should work together to achieve the desired
effect. The
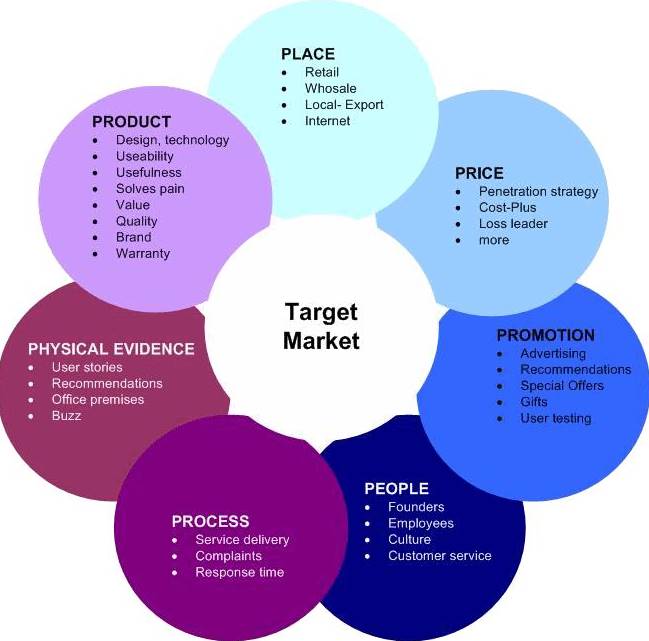
Services Marketing Mix consists of a set of tactics that a company can use to
promote and encourage potential customers to buy their service. The Services
Marketing Mix is also known as the 7 P’s of Marketing. PRODUCT The
design, technology, quality, accessories, branding, and packaging play an
essential role in the product and that is why they are one of the most
significant factors of 7P’s of Service Marketing. Good packaging
automatically puts across the right image in the customer’s mind. It improves
brand utility and awareness. PRICE The price
of your product(s) or service(s) should be based on the market research
conducted during the market analysis and competitor analysis. The aim of
pricing is to ensure that the business generates sufficient sales to achieveprofitability and sustainability. Ensure that you keep
your costs down as much as possible so that you will have room to vary your
selling price(s) within an acceptable range. PLACE (BUSINESS LOCATION) If you are
a retail operation you must select a business location that is easily
accessible by your customers and supports walk by/drive by drop‐in customers. A retail business
is an essential linkage within the marketing channel and the location has to
be chosen strategically. A business with an attractive set‐up and front can be a good
selling location. When identifying a location for your business you need to
build upon your initial market research, a description of potential buyers
and the nature of the product. PROMOTION Promotion
concerns the rangeof methods used by business to
communicate with its potential and current customers, employees and any other
interested party in your products and services. Informing potential customers
about your product(s), its benefits and how to attract customers to buy from
you is crucial. PEOPLE These are
the customers, employees, suppliers, management, partners and all other
stakeholders impacted by your business. It is how you treat them and how
others see them being treated. It is reflected in the values that your
company embraces and demonstrates in your day to day business operation and
interaction with people. People is business. PROCESS This will
include the processes required to provide different services or products to
the customers and understanding of the effectiveness of these processes is
very crucial. E.g. is it car delivery service, drive through window service,
courier delivery, etc. This includes packaging and other operational
efficiencies. PHYSICAL/AMBIENCE
(EVIDENCE) This
refers to the experience of using a product or service. This can be
demonstrated through the provision of information to customers, so that they
can understand more about the product or service at hand. Expert testimonial,
demonstrations and examples of successful implementation are ways to
demonstrate the usefulness of the product or service. Such information can be
provided in the form of brochures, pamphlets, symbols and webinars. Livery
and Artifacts add value to the place Note:Very soon there will be 8Ps
(Performance) A NEW MARKETING MODEL There are
a few different ways in which marketing mix is presented. During the 1950s
the components of the marketing mix were conceived as the 4 Ps. Now 7P’s have
served marketers well for generations, but new innovations can disrupt even
the most established concepts. A new framework is taking hold in marketing
–the 4 C’s. In this model, each of the C words replaces one of the
P’s, flipping the model from the perspective of the marketer to that of the
customer. In the new model: 1.
Consumer/Client replaces Product: Products solve a need for a
customer; by focusing on the consumer in the 4 C’s model, the point of view
changes to a customer/client -based perspective and also allows for the
inclusion of services, which are purchased about as often as physical
products. The consumer/client can mean an internal or external. Internal
buyer can be the worker, manager who buys within and the external buyer can
include the supplier or financier who buyers from your company. 2.
Convenience rather than Place: Both words speak to the same
point –where can my customers obtain my product or service? But in an age where so
many products and services are sourced online, the word “convenience”
incorporates more than just a physical location, as was implied by the word “place”. 3.
Cost takes the place of Price: From the standpoint of the buyer,
the price charged by the seller becomes their cost. Moving to the
word “cost” results in seeing things from the perspective of
the customer, consistent with other aspects of the model. 4.
Communication replaces Promotion: In its most basic form,
promotion is about informing potential customers so that they will recognize the
value in a product or service and part with the funds necessary to obtain it.
However, the word “promotion” also has taken on the context of a deal or
discount. By moving to the word “communication”, the new model
incorporates all forms of reaching customers, whether through advertising,
coupons, social media campaigns, and many others. This includes the processwhich is transporting products to
consumers. Evolving Definitions of the Marketing
Mix During the
1950s the components of marketing mix were conceived as the “four Ps” and
were defined as follows: 1.
Product: the goods and services offered 2.
Promotion: communication and information 3.
Place:
distribution or delivery 4.
Price: ensuring
fair value in the transaction Overtime
three more Ps’ have been added and these are: 5.
Process: activities taking place for the product to reach the consumer 6.
People: all
stakeholders including customers, suppliers, etc. 7.
Physical evidence: the ambience of the business place However, innovation has brought in new
categories of the marketing mix. Most are more consumer oriented and attempt
to better fit the movement toward a marketing orientation and a greater
emphasis on customer value. One example is the four Cs, proposed by
Robert F Lauterborn in 1990: 1.
Customer solution: what the customer wants and needs 2.
Communication: a two-way dialogue with the customer 3.
Convenience: an easy process to act or buy 4.
Cost: the customer’s cost to satisfy that want or need
Marketing concept Marketing
concept is the philosophy that companies should examine the requirements of
their customers and then make decisions to satisfy those needs in a better
manner than the competitors. Today,
most of the companies have adopted various marketing concepts, but this has
not always been the case. The following are the marketing concepts: Production
Concept –indicates
the production orientationof the firm the more we make,
the more profitable it becomes. Product
concept-The idea
that consumers will favour products that offer the
most quality, performance, and features and that the organisation
should therefore devote its energy to making continuous product improvements.
The focus is on developing superior productse.g.
M/Benz Societal
marketing concept -is the
idea that a company’s marketing decisions should consider consumer wants,
needs and intentions of the target market and deliver the expected
satisfaction more effectively and efficiently than the competitorsin
a way to preserve or enhance the consumer’s and society’s wellbeing. Sales
Concept –customers
will not buy enough of the firm’s products unless they are persuaded to do so
through selling effort. Marketing
Concept –success
lies in the company’s ability to create, deliver and communicate a better value
proposition through its marketing offer in comparison to the competitors for
its chosen target segment. Below is
the summarized Marketing Concept
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||