Numbering System
|
Number System in Mathematics Lecturer: Joseph Hamahuwa The
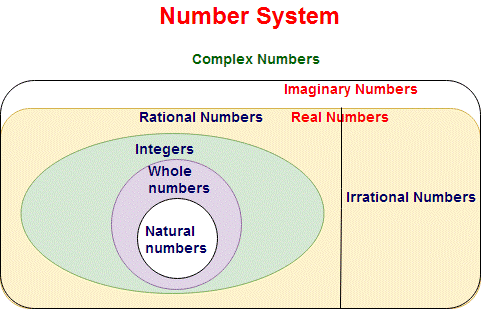
number system mainly into classified into 8 types. o
Complex numbers o
Imaginary numbers o
Real numbers o
Rational numbers o
Irrational numbers o
Integers o
Whole numbers o
Natural numbers Lets
debate: Who is the greatest? Complex
numbers: Every number in number system taken as a
complex number Imaginary
Number: A number that does not exist in the number
line is called imaginary number. For example, square root
of negative numbers are imaginary numbers. It is denoted by i or j i.e √-1 = i i2 = 1 So
there is no real number i that satisfies the above
equation. The quantity i
is called the unit imaginary number. Real
numbers: All numbers that can be represented on the
number line are called real numbers. The
real numbers is the set of numbers containing all of the rational numbers and
all of the irrational numbers. The real numbers are all the numbers on the
number line. Real
Numbers are denoted by R. Rational
numbers: A rational number is defined as number of
the form x/y where x and y are integers and Y # 0. i.e Any number
which can be expressed as in the form of p/q where p and q are the
integers and q # 0 The
set of rational numbers encloses the set of integers and fractions. The
rational numbers that are not integral will have decimal values. These values
can be of two types Terminating
decimal fractions (finite decimal factors): For example 1/5 = 0.5 , 13/5 = 2.6. Non-Terminating
decimal fractions: The nonterminating
decimal fractions having two types. Non
terminating periodic fractions Non
terminating non periodic fractions Non
terminating periodic fractions: These
are nonterminating decimal fractions: 19/6
= 3.16666666
.. 18/7 = 2.57142857142857
. 21/9=
2.3333
. Irrational numbers: An
Irrational numbers are nonterminating and nonperiodic
fractions. i.e. irrational number is a number that
cannot be written as a ratio x/y form (or fraction). In decimal form,
is never ends or repeats. Examples for irrational
numbers are √2 = 1.414213
, π = 3.14159265
., √3, √5
etc. Integers ( numbers having no decimals ) All
numbers that do not having the decimal places in them are called integers. All
whole numbers including Negative number + Positive number Z = {∞
..-5,-4,-3,-2,-1,0,1,2,3,4,5
.∞} i.e the integer it may positive or negative or zero. The
set of integers generally written Z for short. Any
integers are added, subtracted, or multiplied the result is always is an
integer. When
any integers multiplied , each of the multiplied
integer is called a factor or divisor of the resulting product. Whole
numbers : The
set of whole numbers means narrator numbers and 0 Whole
numbers = W = { 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,
..∞} Natural
Numbers: The counting numbers start with 1 and their
end is not defined. Generally it is denoted by N .i.e N ={1,2,3,4
.∞} Another Some important number system : Negative integers Non Negative integers Positive integers Non positive integers Prime numbers Composite numbers Even and Odd numbers Perfect number. Negative
integers: The
integer is less than zero than it is called negative integer. i.e the set of integers { -1,-2,-3,-4,-5
.∞} is
called negative integers. The
product of any two negative integers is always positive integer Non
Negative integers: The
set of numbers Zero and natural numbers is
called non negative integers. i.e. {01,2,3,4
.∞} Positive integers: The
integer is greater than zero than it is called positive integer. The set of
natural numbers is called non negative integers. The
product of any two positive integers is always positive integer. The
product of any two positive and negative integers is always negative integer. i.e the set of numbers {01,2,3,4
.∞} Non positive integers: The
integer is less than zero and include zero than it is called non positive
integer. The
set of numbers { 0,-1,-2,-3,-4,-5
.∞} is
called non positive integers Prime numbers: A
natural number larger than unity is a prime number and it does not having any
other divisors except for unity and itself is called a prime number For example : 2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19
.. 1 is not a prime number. 2 is the only even and lowest prime number. Any
prime number more than 6 than, it comes reminder 1 or 5 when that number is
division by 6. Any
prime number more than 5 , that prime number square division by
24 than reminder comes always 1 If p
and q are any two prime numbers than p2+q2 and p2 -q2are composite numbers. Prime
number exactly having two different factors. No.
of prime numbers from 1 to 50 = 15 No.
of prime numbers from 1 to 100 =25. No.
of prime numbers from 1 to 200 =46 No.
of prime numbers from 1 to 1000 =168 Composite
numbers: A
number having one more divisor apart from 1 and itself is called composite
number. i.e The composite number having atleast
three divisors. In
the mathematical term any composite number n can be expressed as n =
m1a x m2b x m3c x m4d Here
m1, m2, m3 , m4, are the prime numbers and a.b,c,d are the natural numbers. For
example 80 = 51 x 24 i.e When two or more numbers having no common prime
factors apart from the number 1″ , they are called co-prime or
relatively prime to each other. Two
consecutive odd numbers are always co-prime numbers ( Ex : 9
& 11 , 15&17, 21&23
etc ) Two
prime numbers are always prime numbers ( Ex : 3& 7, 11&17,
..etc ) One
prime number and another composite number (Such composite number is not a
multiple of the prime number ) are always co-prime
numbers. This rule exception only for 17 &51. ( Ex : 3 & 16, 4&
9,
.. etc ) Three
or more numbers being co-prime with each other means that all possible pairs
of the numbers would be co- prime with each other. ( Ex: Thus 51, 53
and 55 are co prime each other than the pairs
51&53, 53&55 , 51&55 are also co-prime numbers) Three
consecutive odd numbers are all ways being co-prime numbers. ( Ex : 21,23& 25, 31,33&35
etc.) Even and Odd numbers: A
number which is a multiple of the number 2 than it is called even number.
The even number can be represented by 2n . here n is natural number. A
number which is not multiple of the number 2 than it is called odd number.
The odd number can be represented by 2n+1 . here n is natural number. Operation
of Even and Odd numbers: Odd x
Odd = Odd Odd +
Odd = Even Odd
Odd = Even Odd /
Odd = Odd Even
+ Even = Even Even
x Even = Even Even
even = Even Even
/ Even = Even or Odd Odd x
Even = Even Odd +
Even = Odd Even/
Odd = Even Odd /
Even = Not divisible. Perfect number: Any
number is called perfect number, if the sum of all its factors excepting
itself is equal to the number itself . For
example take a numbers 6. Factors of 6 are 1,2,3,6 Sum
of the factors except itself = 1+2+3 = 6 So
the number 6 is called perfect number. |